Hive与传统数据库对比
| Hive | 传统数据库 | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询语言 | HQL | SQL |
| 数据存储 | HDFS | Raw Device或者 Local FS |
| 数据格式 | 用户自定义 | 系统决定 |
| 数据更新 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 执行 | MapReduce | Excutor |
| 执行延迟 | 高 | 低 |
| 处理数据规模 | 大 | 小 |
| 索引 | 0.8版本后加入位图索引 | 有复杂的索引 |
| 可扩展性 | 高 | 低 |
| Hive | 传统数据库 | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询语言 | HQL | SQL |
| 数据存储 | HDFS | Raw Device或者 Local FS |
| 数据格式 | 用户自定义 | 系统决定 |
| 数据更新 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 执行 | MapReduce | Excutor |
| 执行延迟 | 高 | 低 |
| 处理数据规模 | 大 | 小 |
| 索引 | 0.8版本后加入位图索引 | 有复杂的索引 |
| 可扩展性 | 高 | 低 |
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41851454/article/details/79938811
node ip+port
resource maneger +8088
namenode +50070/9870/9871
4040: 是一个运行的Application在运行的过程中临时绑定的端口,用以查看当前任务的状态.4040被占用会顺延到4041.4042等.4040是一个临时端口,当前程序运行完成后, 4040就会被注销哦。当使用spark交互工具,如spark-sql,spark-shell
8080: 默认是StandAlone下, Master角色(进程)的WEB端口,用以查看当前Master(集群)的状态
18080: 默认是历史服务器的端口, 由于每个程序运行完成后,4040端口就被注销了. 在以后想回看某个程序的运行状态就可以通过历史服务器查看,历史服务器长期稳定运行,可供随时查看被记录的程序的运行过程.
配置历史服务器
https://blog.csdn.net/Heitao5200/article/details/79674684
https://blog.csdn.net/yu0_zhang0/article/details/80396080
注意端口号和hadoop一致,9000->8020
Apache Flink runs the dashboard on port 8081. Since this is a common port there might be conflict with some other services running on the same machines
port和端口可以在flink/conf/flink-conf.yaml 中查看
端口9083
16010
DataFrame支持两种风格进行编程,分别是:
DSL称之为:领域特定语言。
其实就是指DataFrame的特有API
DSL风格意思就是以调用API的方式来处理Data
比如:df.where().limit()
SQL语法风格
SQL风格就是使用SQL语句处理DataFrame的数据
比如:spark.sql(“SELECT * FROM xxx)

步骤:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43665254/article/details/112379113
https://blog.csdn.net/sunflower_sara/article/details/104044412
1、定义函数
2、注册函数
3、使用函数
1 | from pyspark.sql.functions import col, lit |
算子就是分布式集合对象的api
rdd算子分为两类:1.transformation 2.action
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45271668/article/details/106441457
https://blog.csdn.net/Android_xue/article/details/79780463
https://chowdera.com/2022/02/202202091419262471.html
两种共享变量:广播变量(broadcast variable)与累加器(accumulator)
广播变量解决了什么问题?
分布式集合RDD和本地集合进行关联使用的时候, 降低内存占用以及减少网络IO传输, 提高性能.
累加器解决了什么问题?
分布式代码执行中, 进行全局累加
1 | sc = spark.sparkContext |
1 | 55 |
累加器和reduce都可以得到聚合结果,效率???谁先执行 谁短,怎么衡量
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43810802/article/details/120772452
https://blog.csdn.net/zhuzuwei/article/details/104446388
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40161254/article/details/103472056
Use reduceByKey instead of groupByKey
groupByKey creates a lot of shuffling which hampers the performance, while reduceByKey does not shuffle the data as much
1 | in: |
聚合的作用
注意点就是 a,b 操作后的数据类型和a,b保持一致,举个例子 a+b 和a ,b类型一致,否则(a+b)+c会报错
1 collect
collect()
返回包含此RDD中的所有元素的列表
注意:因为所有数据都会加载到driver,所有只适用于数据量不大的情况
2 first
first()
返回RDD中的第一个元素
3 take
take(num)
取RDD的前num个元素
4 top
top(num, key=None)
排序
Get the top N elements from an RDD
5 foreach
foreach(f)
Applies a function to all elements of this RDD 分区输出
1 | def f(x): |
Hive和Spark 均是“分布式SQL计算引擎”,mysql等不是,mysql跑单机上
均是构建大规模结构化数据计算的绝佳利器,同时SparkSQL拥有更好的性能。目前,企业中使用Hive仍旧居多,但SparkSQL将会在很近的未来替代Hive成为分布式SQL计算市场的顶级
1 union ,union all
https://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/sql_union.asp
1 | select 'mobile' as platform union |
2 join
left join 、right join、 inner join,FULL OUTER JOIN,默认join 为 inner join
https://www.cnblogs.com/ingstyle/p/4368064.html
1 | #多个left join |
1 | from Trips T1 |
3.from student A,student B,student C
将三个 student 表相互连接成一个
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangyj_315/article/details/2249209
1 group by
1.group by columns1,columns2
按照字段分组,多个字段看成整体, 分完每组就一行,取每组第一行数据
2.+条件判断
Having
having 子句的作用是筛选满足条件的组,不是在组内选行
在 SQL 中增加 HAVING 子句原因是,WHERE 关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用。
3.注意
有时候不能取第一行,怎么解决?1070. 产品销售分析 III
a 可以先排序,把目标行变成第一行 可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/shiyong1949/article/details/78482737 好像不行
b 使用开窗函数解决,可以
嵌套
http://c.biancheng.net/sql/sub-query.html
1 | select a.Score as Score, |
as后加别名,也可不要as
关键字like
通配符
https://www.cnblogs.com/Leophen/p/11397621.html
1 | select * from table where name like "%三%" |
1.IF
表达式:IF( condition, valua1, value2 )
条件为true,则值是valua1,条件为false,值就是value2
2 case
input几行output几行
一行一行来
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/240717732
两种形式:
1 | --type1 |
then后面多个值
then 1 可
then (1,1) 不可
where xx in (1,1)可
3 where
1 | # Write your MySQL query statement below |
4 判断
1 in
(E1.id , E1.month) in ((1,8))
2 BETWEEN AND
BETWEEN ‘2019-06-28’ AND ‘2019-07-27’
3 EXISTS
用于判断查询子句是否有记录,如果有一条或多条记录存在返回 True,否则返回 False。
1 | SELECT column_name(s) |
1.空字符和null的区别
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42214393/article/details/80463912
2.判断NULL
is not NULL
!=NULL 有问题
ifnull(sum(quantity), 0)
3 和 in、not in结合时
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22592457/article/details/108024521
1 大小判断
available_from < ‘2019-05-23’
datediff(date1,date2)
2 格式转化
DATE_FORMAT()
https://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/func_date_format.asp
1 distinct
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangzehai2234/article/details/88361586
1 | select distinct expression[,expression...] from tables [where conditions]; |
在使用distinct的过程中主要注意一下几点:
distinct , count 一起用
1 | ##建表 |
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29168493/article/details/79149132
查看当前数据库状态,可以统计当前数据库不同语句的执行频次
获取sql执行计划,结果明细参考
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1093229
http://m.biancheng.net/sql/transaction.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372330656
https://medium.com/swlh/recursion-in-sql-explained-graphically-679f6a0f143b
https://www.sqlservertutorial.net/sql-server-basics/sql-server-recursive-cte/
1 | WITH expression_name (column_list) |
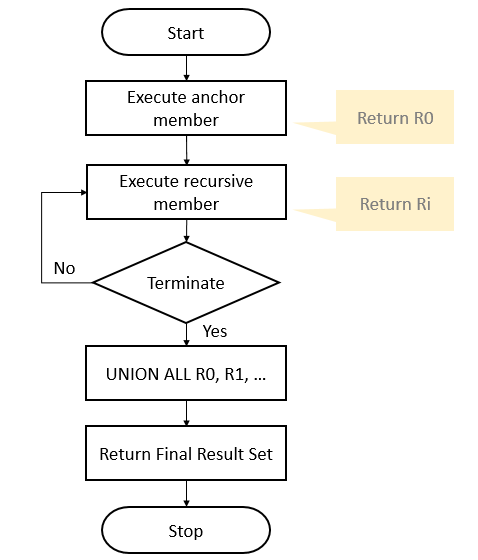
分析 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372330656
R0 :
1 | SELECT UserID,ManagerID,Name,Name AS ManagerName |
| userid | managerid | name | managername |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -1 | boss | boss |
R1:
1 | SELECT c.UserID,c.ManagerID,c.Name,p.Name AS ManagerName |
此时Employee为完整的,cte为
| userid | managerid | name | managername |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -1 | boss | boss |
得到结果为
| c.userid | c.managerid | c.name | c.managername | p.userid | p.managerid | p.name | p.managername |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 1 | A1 | A1 | 1 | -1 | boss | boss |
| 12 | 1 | A2 | A2 | 1 | -1 | boss | boss |
| 13 | 1 | A3 | A3 | 1 | -1 | boss | boss |
1 | SELECT c.UserID,c.ManagerID,c.Name,p.Name AS ManagerName |
| userid | managerid | name | name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 1 | A1 | boss |
| 12 | 1 | A2 | boss |
| 13 | 1 | A3 | boss |
R2,R3…
最后union all R0,R1,R2,。。。
1 | SELECT 1,-1,N'Boss' |
1 -1 Boss —字段
1 -1 Boss
11 1 A1
12 1 A2
13 1 A3
111 11 B1
112 11 B2
121 12 C1
Common Table Expression
with …as…
就是做了某些操作,自动触发的行为
触发器是自动执行的,当用户对表中数据作了某些操作之后立即被触发。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48033173/article/details/111713117
https://blog.csdn.net/hguisu/article/details/5731629
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/10/a-detailed-guide-on-sql-query-optimization/
https://blog.devart.com/how-to-optimize-sql-query.html#sql-query-optimization-basics
https://www.cnblogs.com/feiling/p/3393356.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/03968ac9d8ad
https://blog.csdn.net/happyheng/article/details/53143345
https://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-index.html
https://blog.csdn.net/wangfeijiu/article/details/113409719
可以提高查询效率
和主键的区别,主键是特殊的索引,索引不一定是主键
https://blog.csdn.net/krismile__qh/article/details/98477484
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_33375360/article/details/113371197
既然有主键为啥还要索引,关键在于这是两个东西,一个是为了唯一表示,一个是为了提高查询效率,底层也不同
https://cache.one/read/17347789
聚集索引与非聚集索引
http://c.biancheng.net/view/7366.html
1、创建索引
创建表时指定索引
1 | drop TABLE if EXISTS s1; |
创建表后
CREATE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名(列的列表);/ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD INDEX 索引名 (列名1,列名2,…);
在navicat也可以指定索引
2、删除索引
DROP INDEX index_name ON talbe_name
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX index_name
3、查看索引
SHOW INDEX FROM table_name;
4、使用索引
建立了索引,底层查询效率变高了
查询语句编写上和原来一样,没有区别
https://blog.csdn.net/lenux2017/article/details/80086265
https://www.cnblogs.com/technologykai/articles/14172224.html
https://blog.csdn.net/talentluke/article/details/6420197
http://m.biancheng.net/sql/create-view.html
视图为虚拟的表,包含的不是数据而是sql查询
视图和表的主要区别在于:
作用
使用视图的时候跟表一样
和cte的区别
https://blog.csdn.net/happyboy53/article/details/2731420
子查询包含的是数据,将数据存在内存,而视图包含的不是数据而是sql查询
SQL 语言层面的代码封装与重用
单行函数:单入单出
多行函数:多入单出,最常见的就是聚合函数
应该不存在单入多出,多入多出可以简化为单入单出的多次
https://blog.csdn.net/lailai186/article/details/12570899
注意:
多行,单行结果组合返回一行
例子:select column1 ,count(column2) ,只返回一行
问题来了,多多不一样呢,比如3和2,应该不存在
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_23833037/article/details/53170789
顾名思义,将数据聚集返回单一的值
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40456829/article/details/83657396
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000040088969
https://www.51cto.com/article/639541.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43412569/article/details/107992998
作用
行数保持不变
输入多行(一个窗口)、返回一个值
计算过程
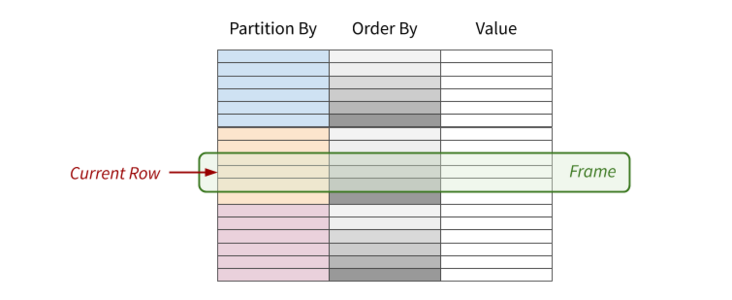
当前行-》分区-》排序-》范围-》计算-》结果填入当前行
语法
1 | window_function ([expression]) OVER ( |
expression
PARTITION BY
表示将数据按 part_list 进行分区, 不加partition by 默认用全部(一个分区)
partition by columns1,columns2
ORDER BY
表示将各个分区内的数据按 order_list进行排序
ROWS / RANGE 决定数据范围
分类
https://www.cnblogs.com/52xf/p/4209211.html
可以分为以下 3 类:
AVG(), COUNT(), MIN(), MAX(), SUM()… 1 | sum(frequency) over(partiton by num ) --分组累加 |
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54494937/article/details/119537881
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-median-given-frequency-of-numbers/
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54494937/article/details/119537881
取值(Value):FIRST_VALUE(), LAST_VALUE(), LEAD(), LAG()…
排序(Ranking):RANK(), DENSE_RANK(), ROW_NUMBER(), NTILE()…
1 | rank() OVER (PARTITION BY Id ORDER BY Month DESC) |
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-cumulative-salary-of-an-employee/
https://blog.csdn.net/a_lllll/article/details/87880389
1 | select distinct C1.seat_id as seat_id |
1 | # Write your MySQL query statement below |
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3aa52ee3a802
https://blog.csdn.net/hjw199089/article/details/77938688
https://blog.csdn.net/mys_35088/article/details/80864092
https://blog.csdn.net/dmy1115143060/article/details/82620715
https://blog.csdn.net/xxd1992/article/details/85254666
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46657040/article/details/108737350
https://blog.csdn.net/heiren_a/article/details/111954523
https://blog.csdn.net/u011564172/article/details/53611109
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22473611/article/details/107822168
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3aa52ee3a802
任务
一个action 一个job
一个job根据rdd的依赖关系构建dag,根据dag划分stage,一个job包含一个或者多个stage
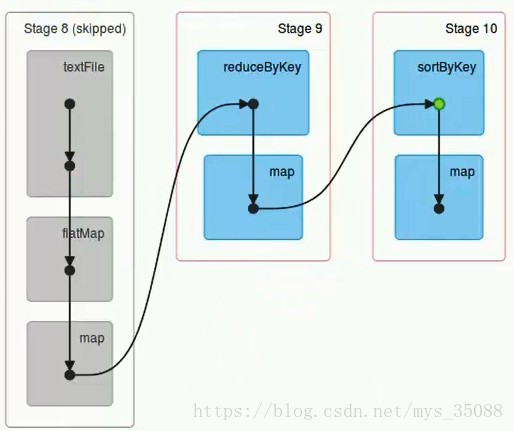
stage根据rdd的分区数决定task数量
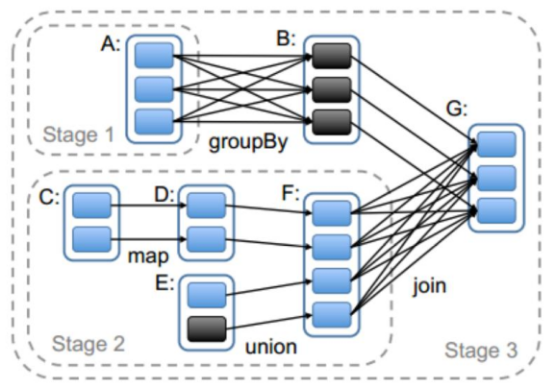
一个task 对应很多record,也就是多少行数据
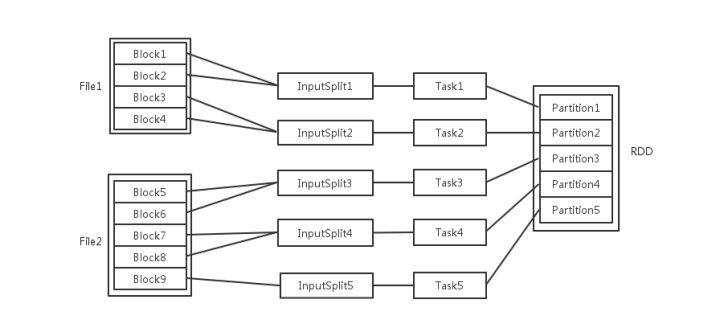
这里应该是 rdd的分区数决定task数量,task数量决定inputsplit数量,然后决定block的组合
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903848536965134
为什么分区?
分区的主要作用是用来实现并行计算,提高效率
分区方式
Spark包含两种数据分区方式:HashPartitioner(哈希分区)和RangePartitioner(范围分区)
分区数设置
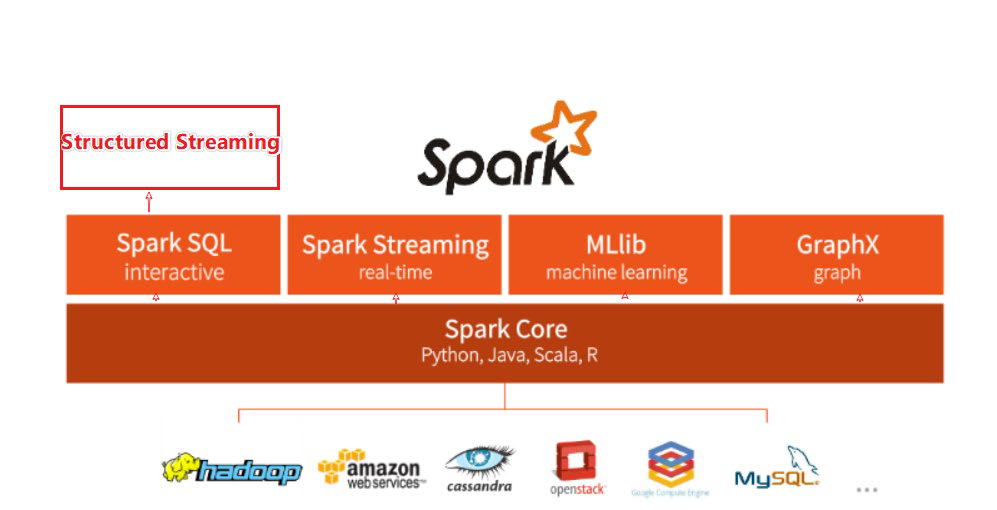
整个Spark 框架模块包含:Spark Core、Spark SQL、Spark Streaming、Spark GraphX、Spark MLlib,而后四项的能力都是建立在核心引擎之上
Spark Core:Spark的核心,Spark核心功能均由Spark Core模块提供,是Spark运行的基础。Spark Core以RDD为数据抽象,提供Python、Java、Scala、R语言的API,可以编程进行海量离线数据批处理计算。
SparkSQL:基于SparkCore之上,提供结构化数据的处理模块。SparkSQL支持以SQL语言对数据进行处理,SparkSQL本身针对离线计算场景。同时基于SparkSQL,Spark提供了StructuredStreaming模块,可以以SparkSQL为基础,进行数据的流式计算。
数据抽象:dataset(Java、Scala) dataframe(Java、Scala、Python、R)
SparkStreaming:以SparkCore为基础,提供数据的流式计算功能。
MLlib:以SparkCore为基础,进行机器学习计算,内置了大量的机器学习库和API算法等。方便用户以分布式计算的模式进行机器学习计算。
GraphX:以SparkCore为基础,进行图计算,提供了大量的图计算API,方便用于以分布式计算模式进行图计算。