spark容错机制
https://blog.csdn.net/JasonDing1354/article/details/46882585
https://blog.csdn.net/dengxing1234/article/details/73613484
容错指的是一个系统在部分模块出现故障时还能否持续的对外提供服务
https://blog.csdn.net/JasonDing1354/article/details/46882585
https://blog.csdn.net/dengxing1234/article/details/73613484
容错指的是一个系统在部分模块出现故障时还能否持续的对外提供服务
PySpark宗旨是在不破坏Spark已有的运行时架构,在Spark架构外层包装一层Python API,借助Py4j实现Python和Java的交互,进而实现通过Python编写Spark应用程序
Hive和Spark 均是“分布式SQL计算引擎”,mysql等不是,mysql跑单机上
均是构建大规模结构化数据计算的绝佳利器,同时SparkSQL拥有更好的性能。目前,企业中使用Hive仍旧居多,但SparkSQL将会在很近的未来替代Hive成为分布式SQL计算市场的顶级
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3aa52ee3a802
https://blog.csdn.net/hjw199089/article/details/77938688
https://blog.csdn.net/mys_35088/article/details/80864092
https://blog.csdn.net/dmy1115143060/article/details/82620715
https://blog.csdn.net/xxd1992/article/details/85254666
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46657040/article/details/108737350
https://blog.csdn.net/heiren_a/article/details/111954523
https://blog.csdn.net/u011564172/article/details/53611109
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22473611/article/details/107822168
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3aa52ee3a802
任务
一个action 一个job
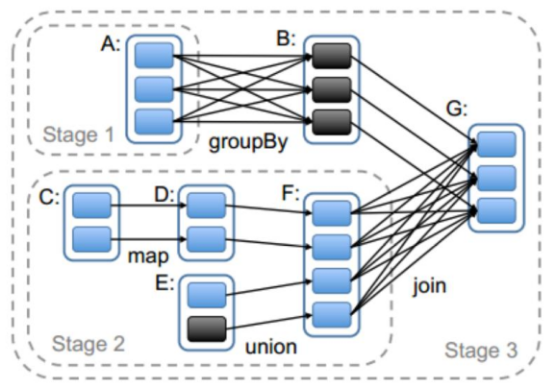
一个job根据rdd的依赖关系构建dag,根据dag划分stage,一个job包含一个或者多个stage
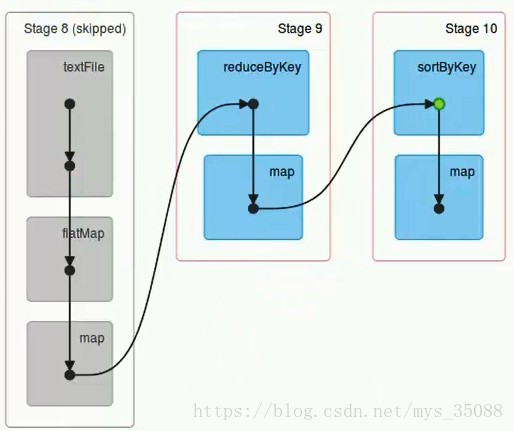
stage根据rdd的分区数决定task数量
一个task 对应很多record,也就是多少行数据
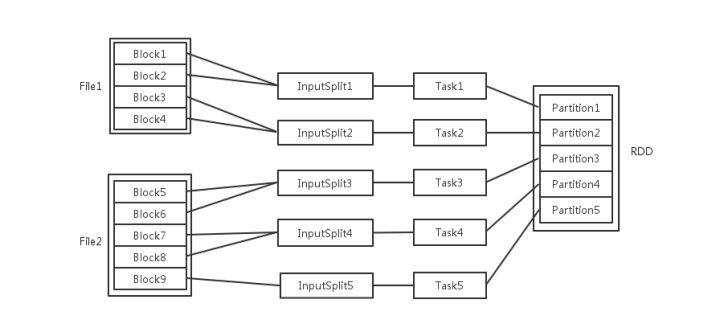
这里应该是 rdd的分区数决定task数量,task数量决定inputsplit数量,然后决定block的组合
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903848536965134
为什么分区?
分区的主要作用是用来实现并行计算,提高效率
分区方式
Spark包含两种数据分区方式:HashPartitioner(哈希分区)和RangePartitioner(范围分区)
分区数设置
https://www.educba.com/mapreduce-vs-spark/
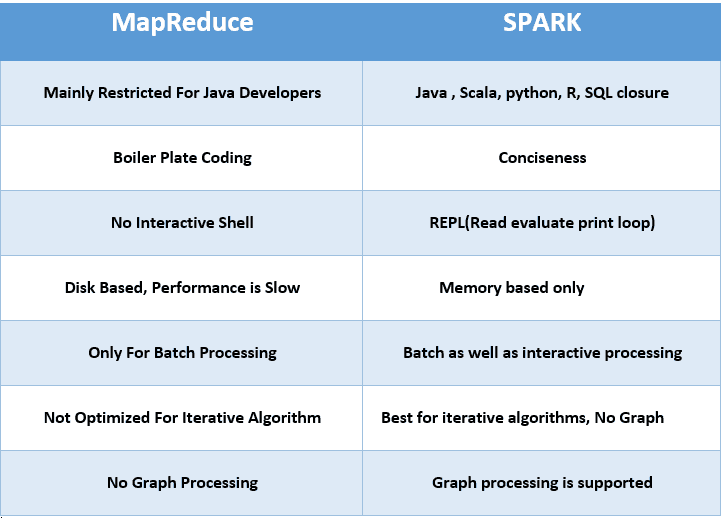
| MapReduce | Spark | |
|---|---|---|
| Product’s Category | From the introduction, we understood that MapReduce enables the processing of data and hence is majorly a data processing engine. | Spark, on the other hand, is a framework that drives complete analytical solutions or applications and hence making it an obvious choice for data scientists to use this as a data analytics engine. |
| Framework’s Performance and Data Processing | In the case of MapReduce, reading and writing operations are performed from and to a disk thus leading to slowness in the processing speed. | In Spark, the number of read/write cycles is minimized along with storing data in memory allowing it to be 10 times faster. But spark may suffer a major degradation if data doesn’t fit in memory. |
| Latency | As a result of lesser performance than Spark, MapReduce has a higher latency in computing. | Since Spark is faster, it enables developers with low latency computing. |
| Manageability of framework | MapReduce being only a batch engine, other components must be handled separately yet synchronously thus making it difficult to manage. | Spark is a complete data analytics engine, has the capability to perform batch, interactive streaming, and similar component all under the same cluster umbrella and thus easier to manage! |
| Real-time Analysis | MapReduce was built mainly for batch processing and hence fails when used for real-time analytics use cases. | Data coming from real-time live streams like Facebook, Twitter, etc. can be efficiently managed and processed in Spark. |
| Interactive Mode | MapReduce doesn’t provide the gamut of having interactive mode. | In spark it is possible to process the data interactively |
| Security | MapReduce has accessibility to all features of Hadoop security and as a result of this, it is can be easily integrated with other projects of Hadoop Security. MapReduce also supports ASLs. | In Spark, the security is by default set to OFF which might lead to a major security fallback. In the case of authentication, only the shared secret password method is possible in Spark. |
| Tolerance to Failure | In case of crash of MapReduce process, the process is capable of starting from the place where it was left off earlier as it relies on Hard Drives rather than RAMs | In case of crash of Spark process, the processing should start from the beginning and hence becomes less fault-tolerant than MapReduce as it relies of RAM usage. |
https://blog.csdn.net/JENREY/article/details/84873874
1 spark基于内存 ,mapreduce基于磁盘
指的是中间结果
MapReduce:通常需要将计算的中间结果写入磁盘,然后还要读取磁盘,从而导致了频繁的磁盘IO
Spark:不需要每次将计算的中间结果写入磁盘
2 spark粗粒度资源申请,MapReduce细粒度资源申请
spark 执行task不需要自己申请资源,提交任务的时候统一申请了
MapReduce 执行task任务的时候,task自己申请
3 spark基于多线程,mapreduce基于多进程
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1624245
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41290471/article/details/106203419
https://www.cnblogs.com/qingyunzong/p/8992664.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/liugp/p/16209394.html#1spark-on-hive
Hive既作为存储又负责sql的解析优化,Spark负责执行
Hive只作为存储角色,Spark负责sql解析优化,执行
hive on spark大体与spark on hive结构类似,只是SQL引擎不同
根据rdd的依赖关系构建dag,根据dag划分stage
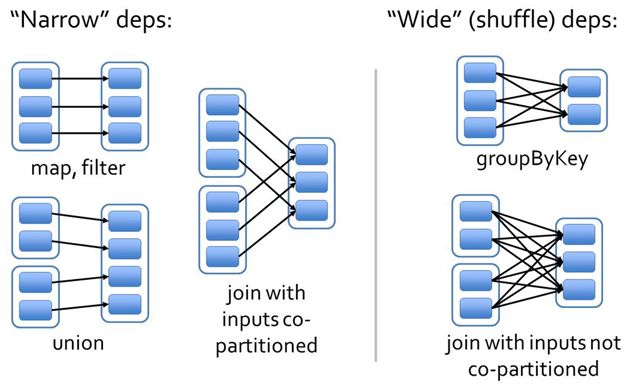
蓝色框是rdd分区
父rdd -> 子rdd
区分宽窄依赖主要就是看父RDD数据流向,要是流向一个的话就是窄依赖,流向多个的话就是宽依赖。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40271036/article/details/79996516
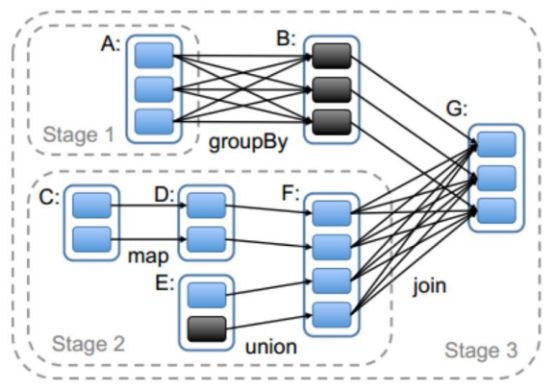
整体思路是:从后往前推,遇到宽依赖就断开,划分为一个stage;遇到窄依赖就将这个RDD加入该stage中
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5c2301dfa360
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67068559
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_49834705/article/details/113111596
https://lmrzero.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106015264?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
为啥宽依赖有shuffle 窄依赖没有shuffle
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37163925/article/details/106260434
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html
https://book.itheima.net/course/1269935677353533441/1270998166728089602/1270999667882074115
通过设置mater来选择部署方式。这是Spark程序需要连接的集群管理器所在的URL地址。如果这个属性在提交应用程序的时候没设置,程序将会通过System.getenv(“MASTER”)来获取MASTER环境变量;但是如果MASTER环境变量没有设定,那么程序将会把master的值设定为local[*]
local为单机
standalone是Spark自身实现资源调度
yarn为使用hadoop yarn来实现资源调度
本地模式就是以一个独立的进程,通过其内部的多个线程来模拟整个Spark运行时环境
local【N】:N为线程数量,通常N为cpu的core的数量
local【*】:cpu的core数量
跑local可以不依赖hadoop
https://blog.csdn.net/wangmuming/article/details/37695619
https://blog.csdn.net/bettesu/article/details/68512570
https://sfzsjx.github.io/2019/08/26/spark-standalone-%E8%BF%90%E8%A1%8C%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86
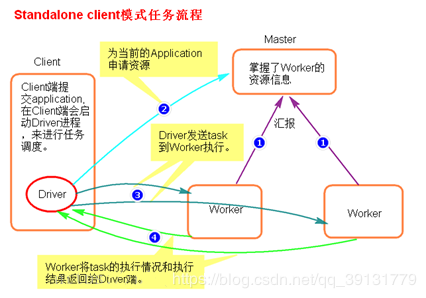
执行流程
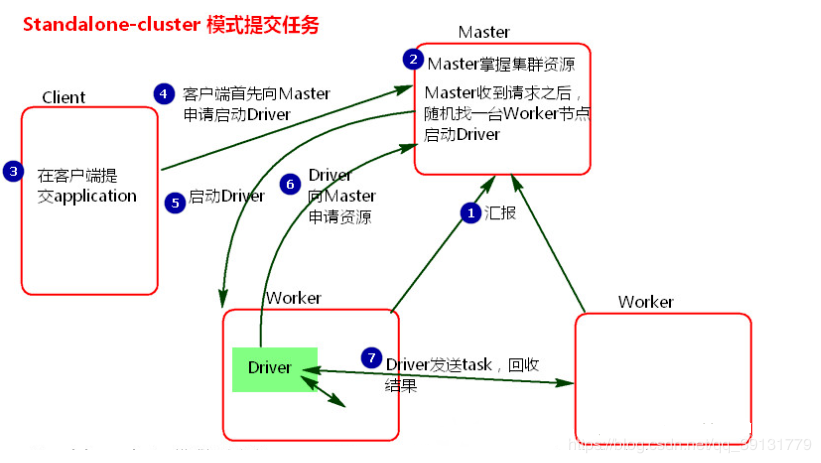
执行流程:
a general cluster manager that can also run Hadoop MapReduce and service applications. (Deprecated)
为什么要YARN?
Spark On YARN是有两种运行模式的,一种是Cluster模式一种是Client模式.这两种模式的区别就是Driver运行的位置.
Cluster模式即:Driver运行在YARN容器内部, 和ApplicationMaster在同一个容器内
Client模式即:Driver运行在客户端进程中, 比如Driver运行在spark-submit程序的进程中
具体流程步骤如下:
1)、任务提交后会和ResourceManager通讯申请启动ApplicationMaster;
2)、随后ResourceManager分配Container,在合适的NodeManager上启动ApplicationMaster,此时的ApplicationMaster就是Driver;
3)、Driver启动后向ResourceManager申请Executor内存,ResourceManager接到ApplicationMaster的资源申请后会分配Container,然后在合适的NodeManager上启动Executor进程;
4)、Executor进程启动后会向Driver反向注册;
5)、Executor全部注册完成后Driver开始执行main函数,之后执行到Action算子时,触发一个job,并根据宽依赖开始划分stage,每个stage生成对应的taskSet,之后将task分发到各个Executor上执行;
具体流程步骤如下:
1)、Driver在任务提交的本地机器上运行,Driver启动后会和ResourceManager通讯申请启动ApplicationMaster;
2)、随后ResourceManager分配Container,在合适的NodeManager上启动ApplicationMaster,此时的ApplicationMaster的功能相当于一个ExecutorLaucher,只负责向ResourceManager申请Executor内存;
3)、ResourceManager接到ApplicationMaster的资源申请后会分配Container,然后ApplicationMaster在资源分配指定的NodeManager上启动Executor进程;
4)、Executor进程启动后会向Driver反向注册,Executor全部注册完成后Driver开始执行main函数;
5)、之后执行到Action算子时,触发一个Job,并根据宽依赖开始划分Stage,每个Stage生成对应的TaskSet,之后将Task分发到各个Executor上执行。
an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.